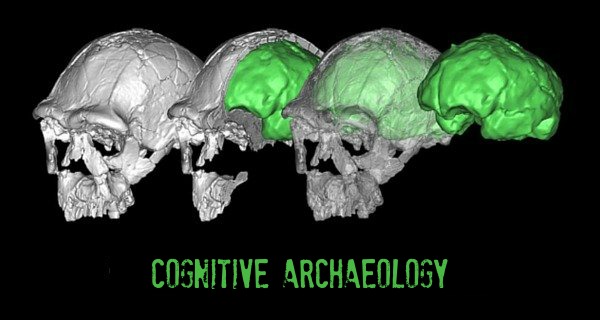
Cognitive Archaeology
What is Cognitive Archaeology?
Cognitive archaeology is a truly interdisciplinary field that applies the theories and methods of several academic domains - cognitive psychology, neuropsychology, archaeology, linguistics and the philosophy of mind/consciousness - in order to explore the evolutionary development of cognition in humans and other primates.
Cognitive archaeology studies the origins and adaptive purposes of such cognitive processes and capabilities as concept formation, spatial cognition, social cognition, language, symbolic structures, and working memory.
(Information courtesy of the Center for Cognitive Archaeology at the University of Colorado, Colorado Springs).
Aspects of Archaeology
Insightful and engaging introduction to cognitive archaeology.
CLICK HERE To read about new evidence suggesting that fire may have influenced the evolution of the human mind.
Essential Reading
In How to Think Like a Neandertal, archaeologist Thomas Wynn and psychologist Frederick L. Coolidge team up to provide a brilliant account of the mental life of Neandertals, drawing on the most recent fossil and archaeological remains. Indeed, some Neandertal remains are not fossilized, allowing scientists to recover samples of their genes - one specimen had the gene for red hair and, more provocatively, all had a gene called FOXP2, which is thought to be related to speech.
Given the differences between their faces and ours, their voices probably sounded a bit different, and the range of consonants and vowels they could generate might have been different. But they could talk, and they had a large (perhaps huge) vocabulary - words for places, routes, techniques, individuals, and emotions. Extensive archaeological remains of stone tools and living sites (and, yes, they did often live in caves) indicate that Neandertals relied on complex technical procedures and spent most of their lives in small family groups. The authors sift the evidence that Neandertals had a symbolic culture - looking at their treatment of corpses, the use of fire, and possible body coloring--and conclude that they probably did not have a sense of the supernatural. The book explores the brutal nature of their lives, especially in northwestern Europe, where men and women with spears hunted together for mammoths and wooly rhinoceroses. They were pain tolerant, very likely taciturn, and not easy to excite.
Wynn and Coolidge offer here an eye-opening portrait of Neandertals, painting a remarkable picture of these long-vanished people and providing insight, as they go along, into our own minds and culture.
See following link for full details.
How To Think Like a Neandertal
Recent Articles
-
Psychology Articles by David Webb
Feb 10, 26 06:31 AM
Discover psychology articles by David Webb, featuring science-based insights into why we think, feel, and behave the way we do. -
Music and Memory: How Songs Shape Identity, Emotion, and Life Stories
Feb 10, 26 06:25 AM
How music and memory intertwine to preserve identity, evoke emotion, and anchor life stories. A psychological look at playlists, nostalgia, and the brain. -
Dr. Jody Carrington Interview | Trauma, Connection, and Mental Health
Feb 04, 26 08:18 AM
Interview with Dr. Jody Carrington on trauma integration, loneliness, burnout, and what it really means to feel seen.
Please help support this website by visiting the All About Psychology Amazon Store to check out an awesome collection of psychology books, gifts and T-shirts.
Go To The Types of Psychology Page
Go From Cognitive Archaeology Back To The Home Page







New! Comments
Have your say about what you just read! Leave me a comment in the box below.